Given an array nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position. Return the max sliding window.
Follow up: Could you solve it in linear time?
Example:
Input: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], and k = 3
Output: [3,3,5,5,6,7]
Explanation:
Window position Max
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5 -10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4 1 <= k <= nums.length
For original task refer to leetcode
Solution
The goal is simple, try to find maximum value in the range of given sliding window for each iteration. There are multiple ways of solving this problem and the worst case is brute-force that gives complexity O(n*k). I will try to solve it using Deque data structure in Java.
Systematic Approach
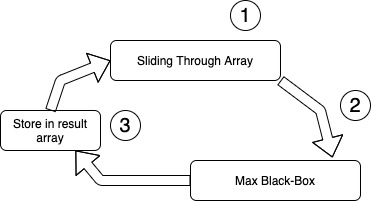
1) Slding over a given nums array
2) Call Max Black-Box for the next element (that goes into window)
3) Store returned result from Max Black-Box
The reason I have called Max Black-Box to clearly divide two processes. So don’t get scared by just name of Black-Box, it is just metaphorical name.
There are two ways of starting the sliding window, the first one is when sliding window starts from very first element. In this case we could just consider that other elements are just not exist
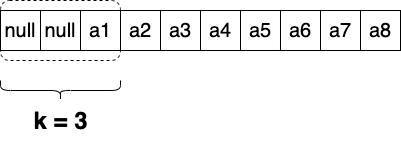
Or we can just fill out all elements till k and then start generating an answer. In this task we need to do exactly that, by starting generate result from k-th element
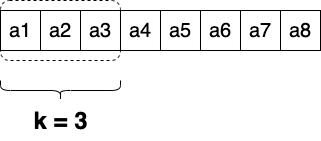
We can describe sliding window process by using two cycles
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] result = new int[nums.length-(k-1)];
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < k;i++) {
result[0] = maxBlackBox(nums,k, i);
}
for (; i < nums.length; i++) {
result[i - k + 1] = maxBlackBox(nums, k, i);
}
return result;
}
In the first for loop we are checking first k-th elements and initializing the process. It is also important that we are feeding the elements into maxBlackBox which is going to track maximum. That is why all results of the first loop stored in the result[0]. In the second loop we are simply sliding over the remaining nums elements and calling maxBlackBox for each new element. maxBlackBox returns maximum value for the range between i-k to i.
Maximum Black-Box
As it has been mentioned before we are using simple deque data structure inside our maximum black-box. It is used to store indexes of nums array
max1_id, max2_id, max3_id, max4_id ...
To solve this problem using deque we have to settle two conditions for our deque data structure.
Condition-1: The values of the indexes in the deque must have decreasing order, means;
nums[max1_id] > nums[max2_id] > nums[max3_id] > nums[max4_id] > ...
Condition-2: Any index in the deque should not be outside of the sliding window, means:
maxN_id > i - k
To put it simply, while window moves right we should guarantee that all indexes outiside the current considered window must be deleted from deque. Efficiency of our solution depends on how efficient we satisfy these two conditions (Condition-1 and Condition-2).
To satisfy those conditions efficiently we have to add new coming element to the right side of the deque. While adding new element to the deque we have to guarantee that last element is greater than new coming element.
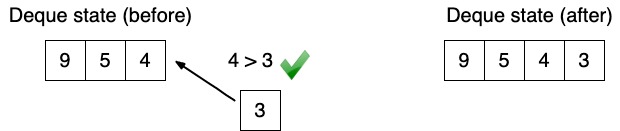
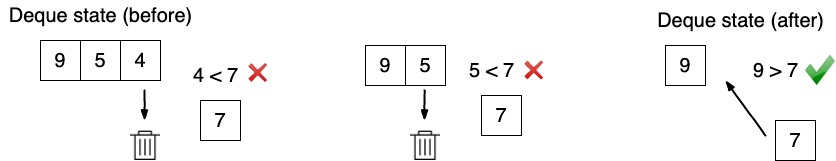
Attention: above I am operations are happening over the values, but we should remember that in deque we are storing indexes of the nums array. Lets put it in code:
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] <= nums[i]) {
deque.removeLast();
}
deque.addLast(i);
!deque.isEmpty() - here we are guaranteeing that deque is not empty, otherwise it will throw NoSuchElementException
To satisfy Condition-2 we have to assure that all indexes in the deque in the range of window. We could simply loop through the elements of the deque and check it. But if we look through code written above, we can see that indexes in the deque are already sorted in a decreasing order.
max1_id < max2_id < max3_id < max4_id < ...
So we can only start comparing from the left side of the deque and stop checking as soon as the index belongs to the range of sliding window. If checked index does not belong to the range we have to remove it from the deque.
while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() <= i - k) {
deque.removeFirst();
}
When both conditions are satisfied we simply peek most left element of the deque and return the value (do not use pop operation)
return nums[deque.peek()];
Full Code
class Solution {
private Deque
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { int[] result = new int[nums.length-(k-1)]; int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < k;i++) { result[0] = maxBlackBox(nums,k, i); }
for (; i < nums.length; i++) {
result[i - k + 1] = maxBlackBox(nums, k, i);
}
return result; }
private int maxBlackBox(int [] nums, int k, int i) { // Shart-2 while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() <= i - k) { deque.removeFirst(); }
// Shart-1
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] <= nums[i]) {
deque.removeLast();
}
deque.addLast(i);
return nums[deque.peek()]; } }
Reference
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sliding-window-maximum-maximum-of-all-subarrays-of-size-k/