Merge sort is another sorting algorithm that applies the divide-and-conquer approach, where the problem is divided into sub-problems recursively. Keep dividing until the subproblem becomes primitive. After that, the results of the divisions are combined and formed the result for the upper caller and so on.
Merge sort algorithms can be described following to divide-and-conquer paradigm:
- Divide: Divide the n-element sequence to be sorted into two subsequences of n/2 elements each
- Conquer: Sort the two subsequences recursively using merge sort
- Combine: Merge the two sorted subsequences to produce the sorted answer
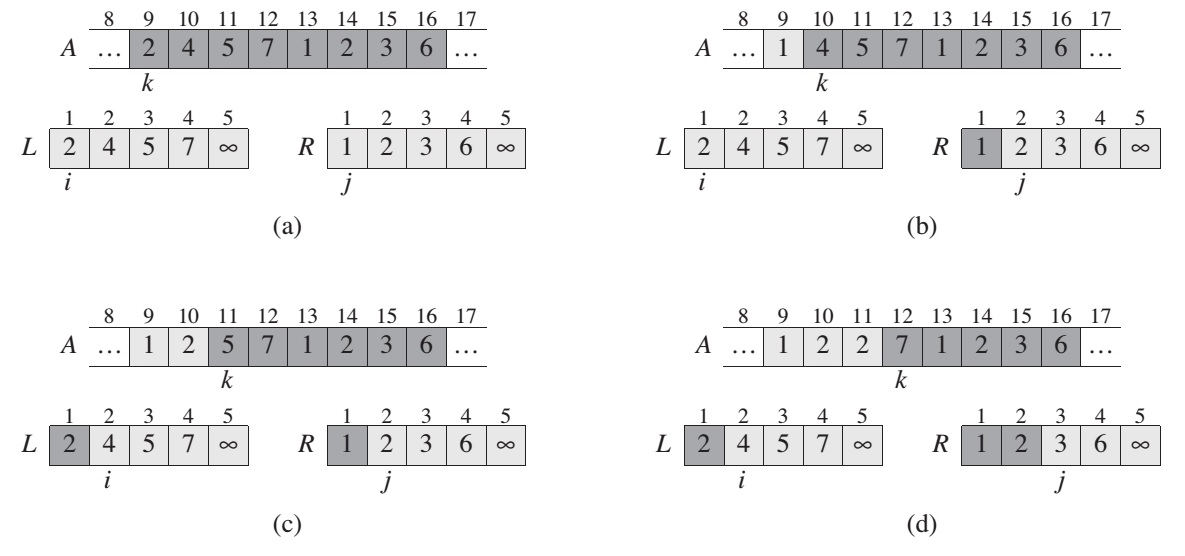
MERGE(A, p, q, r):
n1 = q - p + 1
n2 = r - q
let L[1..n1+1] and R[1..n2+1] be new arrays
for i = 1 to n1
L[i] = A[p+i-1]
for j = 1 to n2
R[j] = A[q+j]
L[n1+1] = infinity
R[n2+1] = infinity
i = 1
j = 1
for k = p to r
if L[i] <= R[j]
A[k] = L[i]
i = i + 1
else A[k] = R[j]
j = j + 1
MERGE-SORT(A, p, r):
if p < r
q = floor((p+r) / 2)
MERGE-SORT(A, p, q)
MERGE-SORT(A, q + 1, r)
MERGE(A, p, q, r)
Sort the entire sequence A = <A[1], A[2], …, A[n]>, we make the initial call MERGE-SORT(A, 1, A.length), where once again A.length = n. Complexity of the merge-sort boils down to: O(n lg n)