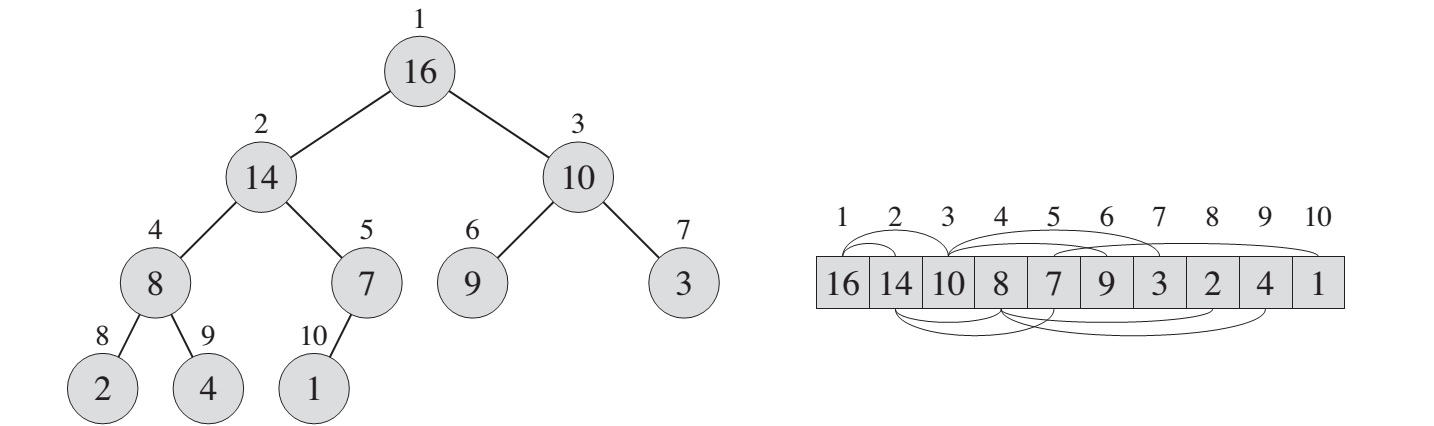
The (binary) heap data structure is an array object that we can view as a nearly complete binary tree. A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Macros functions:
- PARENT(i): return floor(i.2)
- LEFT(i): return 2 * i
- RIGHT(i): return 2 * i + 1
Procedure Functions:
- MAX-HEAPIFY procedure, runs in O(lg n) time, is the key to maintaining the max-heap property
- BUILD-MAX-HEAP procedure, runs in a linear time, produces a max-heap from an unordered input array
- HEAPSORT procedure, runs in O(n lg n) time, sorts an array in place
- MAX-HEAP-INSERT, HEAP-EXTRACT-MAX, HEAP-INCREASE-KEY and HEAP-MAXIMUM procedures, all runs in O(lg n) time. Those procedures are used at implementing a priority queue
Maintaining the heap property
MAX-HEAPIFY is the procedure which is responsible for maintaining the max-heap property. Receives an array A and index i as an input. It simply checks the LEFT(i) and RIGHT(i) child nodes of the given index i for being small. if both childs are are greater than current element then the bigger one is selected, and exchanged the positions with current node. That way the max-heap rule can be supported (max-heap rule: parrent node is bigger than childs)
MAX-HEAPIFY(A,i):
l = LEFT(i)
r = RIGHT(i)
if l <= A.heap-size and A[l] > A[i]
largest = l
else largest = i
if r <= A.heap-size and A[r] > A[largest]
largest = r
if largest != i
exchange A[i] with A[largest]
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, largest)
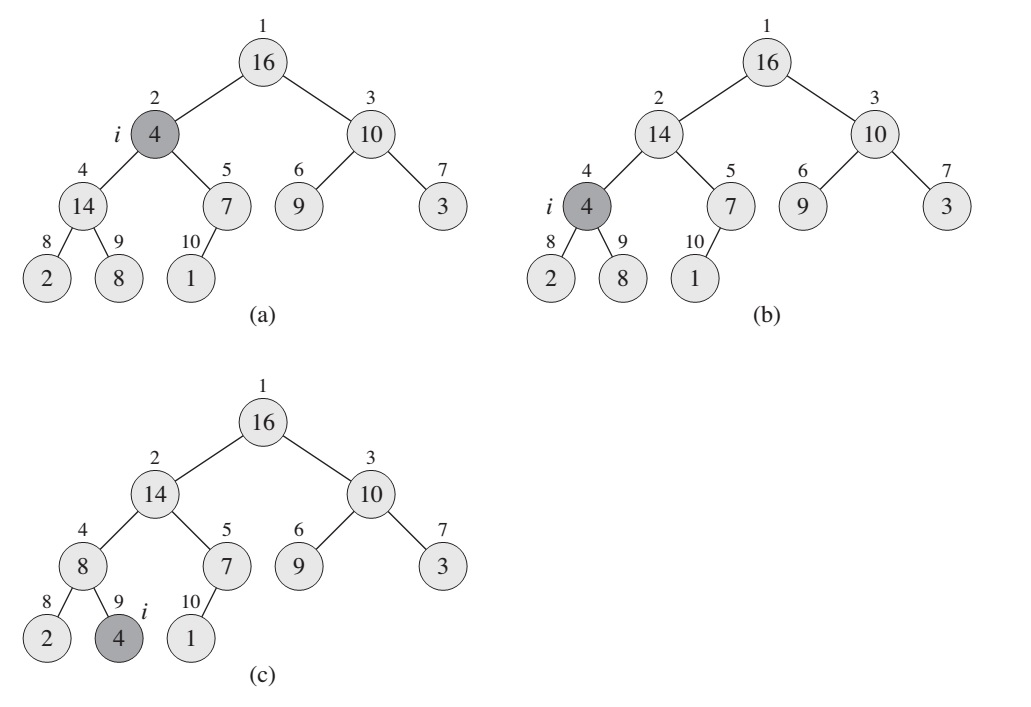
Figure: The action of MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 2), where A.heap-size = 10
The running time of MAX-HEAPIFY on a subtree of size n rooted at a given node i is the O(1) time to fix up the relationships among elements. The children’s subtrees each have a size at most 2n/3. That is why worst case of running time of MAX-HEAPIFY by the recurrence is: T(n) <= T(2n/3) + O(1)
Building a heap
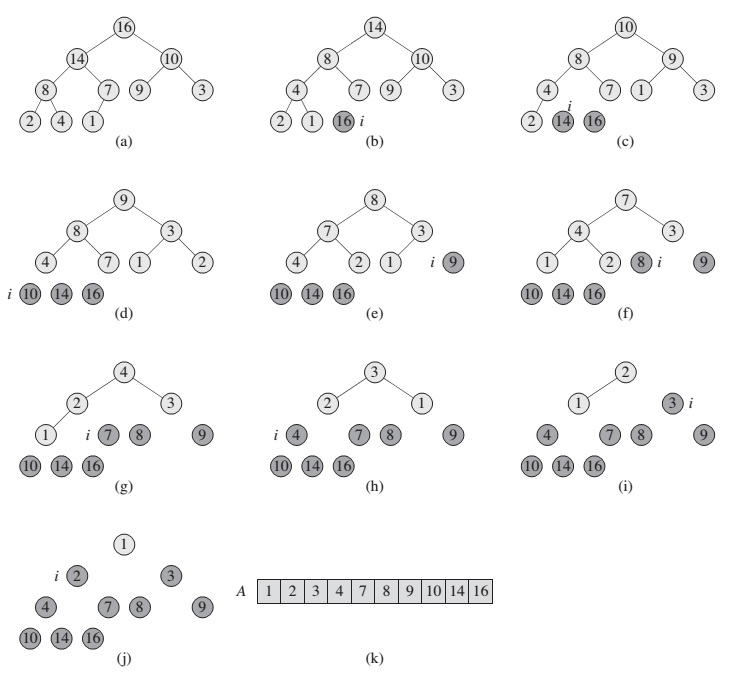
The procedure BUILD-MAX-HEAP goes through the remaining nodes of the tree and runs MAX-HEAPIFY on each one:
BUILD-MEAX-HEAP(A):
A.heap-size = A.length
for i = floor(A.length / 2) downto 1
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, i)
The time required by MAX-HEAPIFY when called on a node of height h is O(h), and so we can express the total cost of BUILD-MAX-HEAP as being bounded from above. Hence, it is possible to build a max-heap from an unordered array in a linear time.
The Heapsort Algorithm
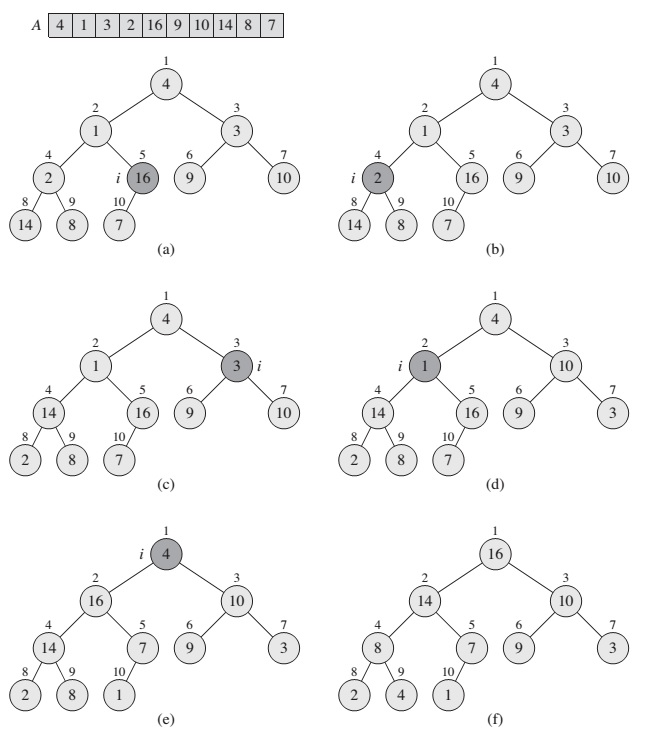
The heapsort algorithm starts with BUILD-MAX-HEAP to build a max-heap on the input array A[1 .. n], where n = A.length. Since the maximum element of the array is stored at the root A[1], we can put it into its correct final position to exchanging it with A[n].
HEAPSORT(A):
BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A)
for i = A.length downto 2
exchange A[1] with A[i]
A.heap-size = A.heap-size - 1
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 1)
The HEAPSORT procedure takes time O(n log n), since the call to BUILD-MAX-HEAP takes time O(n) and each of the n-1 calls to MAX-HEAPIFY takes time O(lg n)
Priority queues
Heap data structure itself has many uses, one of the most popular application of a heap is an efficient priority queue. A priority queue is a data structure for maintaining a set S of elements, each with an associated value called a key.
HEAP-MAXIMUM(A): return A[1]
HEAP-EXTRACT-MAX(A):
if A.heap-size < 1:
error "heap underflow"
max = A[1]
A[1] = A[A.heap-size]
A.heap-size = A.heap-size - 1
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 1)
return max
The running time of HEAP-EXTRACT-MAX is O(lg n), since it performs only a constant amount of work on top of the O(lg n) time for MAX-HEAPIFY
The procedure HEAP-INCREASE-KEY implements the INCREASE-KEY operation. The procedure first updates the key of element A[i] to its new value. Because increasing the key of A[i] might violate the max-heap property,the procedure then, traverses a simple path from this node toward the root to find a proper place for the newly increased key. As HEAP-INCREASEKEY traverses this path, it repeatedly compares an element to its parent, exchanging their keys and continuing if the element’s key is larger, and terminating if the element’s key is smaller, since the max-heap property now holds.
HEAP-INCREASE-KEY(A, i, key):
if key < A[i]
error "new key is smaller than current key"
A[i] = key
while i > 1 and A[PARENT(i)] < A[i]
exchange A[i] with A[PARENT(i)]
i = PARENT(i)
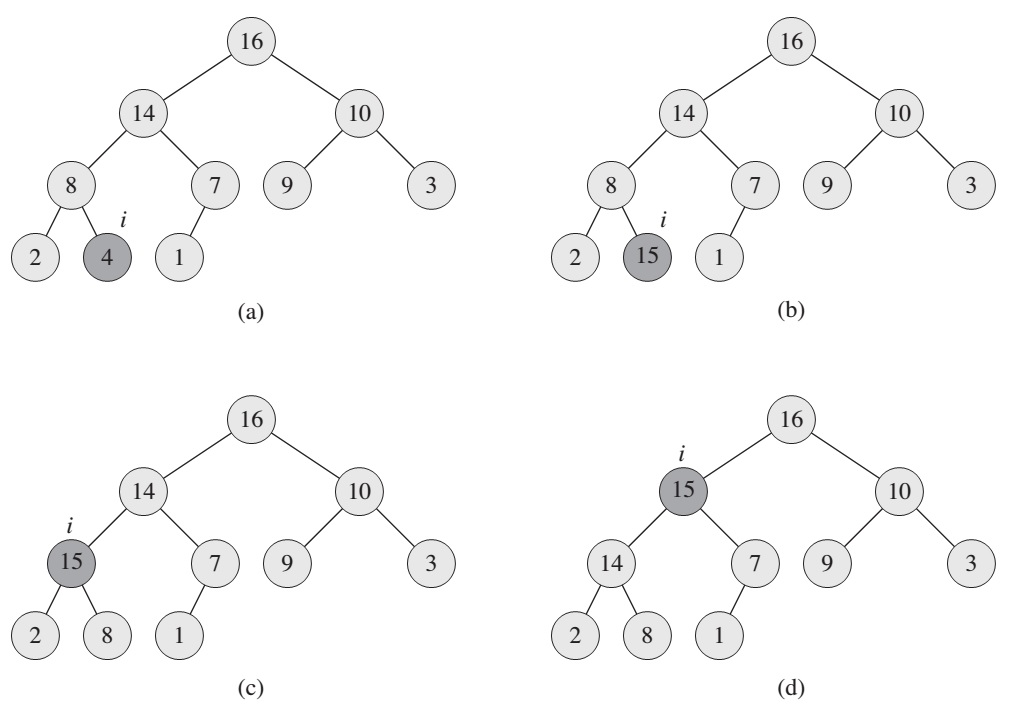
The procedure MAX-HEAP-INSERT implements the INSERT operation. It takes as an input the key of the new element to be inserted into max-heap A.
MAX-HEAP-INSERT(A, key):
A.heap-size = A.heap-size + 1
A[A.heap-size] = -infinity
HEAP-INREASE-KEY(A, A.heap-size, key)
The running time of MAX-HEAP-INSERT on an n-element heap is O(lg n). A heap support any priority-queue operation on a set of size n in O(lg n) time.