Insertion sort, which is an efficient algorithm for sorting a small number of elements. Insertion sort works the way many people do it by hand while playing a card game (Though personally i would not sort the cards while playing, because there are too many skill-full guys, who may take an advantage of it)

Insertion sort
INSERTION-SORT(A):
for j = 2 to A.length
key = A[j]
// Insert A[j] into the sorted sequence A[1..j-1]
i = j - 1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i + 1] = A[i]
i = i - 1
A[i + 1] = key
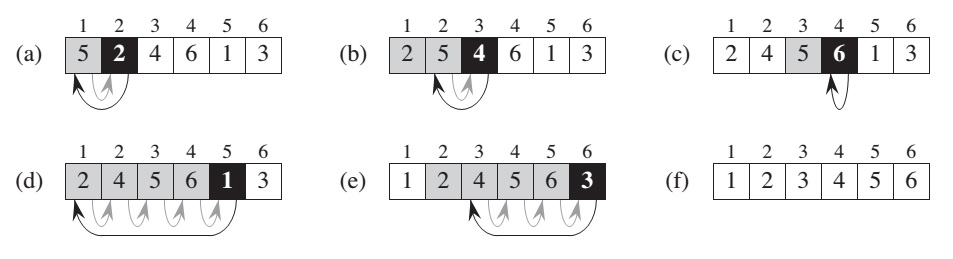
The black rectangle holds the key taken from A[j], which is compared with the values in shaded rectangles to its left.
here formaly we call Loop invariant, when at the each iteration of for loop the subarray A[1..j-1] consists of the elements originally existed in A[1..j-1] subarray, but in sorted order.
Analyzing algorithms
Analyzing an algorithm has come to mean predicting the resources that the algorithm requires.

The running time of the algorithm is the sum of running times for each statement executed.
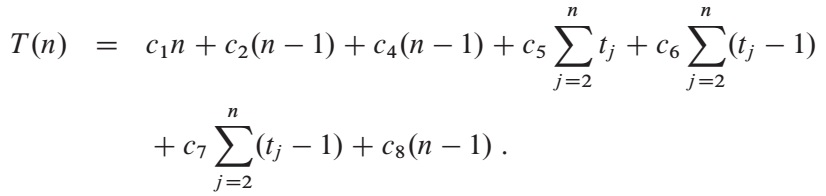
Simplifying abstraction: it is the rate of growth, or order of growth, of the running time that really intersts us. We therefore consider only the leading term of a formula (e.g.,an^2), since the lower-order terms are relatively insignificant for large values of n. We also ignore the leading term’s constant coefficient, since constant factors are less significant than the rate of growth in determining computational efficiency for large inputs.
We write that insertion sort has a worst-case running time of Theta(n^2).