This short blog can be used as a quick cheat-sheet for understanding how Web-browser processes the pages. In general everything in the page should be divided and considered under three sections: DOM objects, CSS objects and JS objects. While browser runs through the page it builds a tree out of objects which is later given to renderer to actually draw a page for user.
To make it easy to imagine following is the figure of that tree (represented in JSON format):
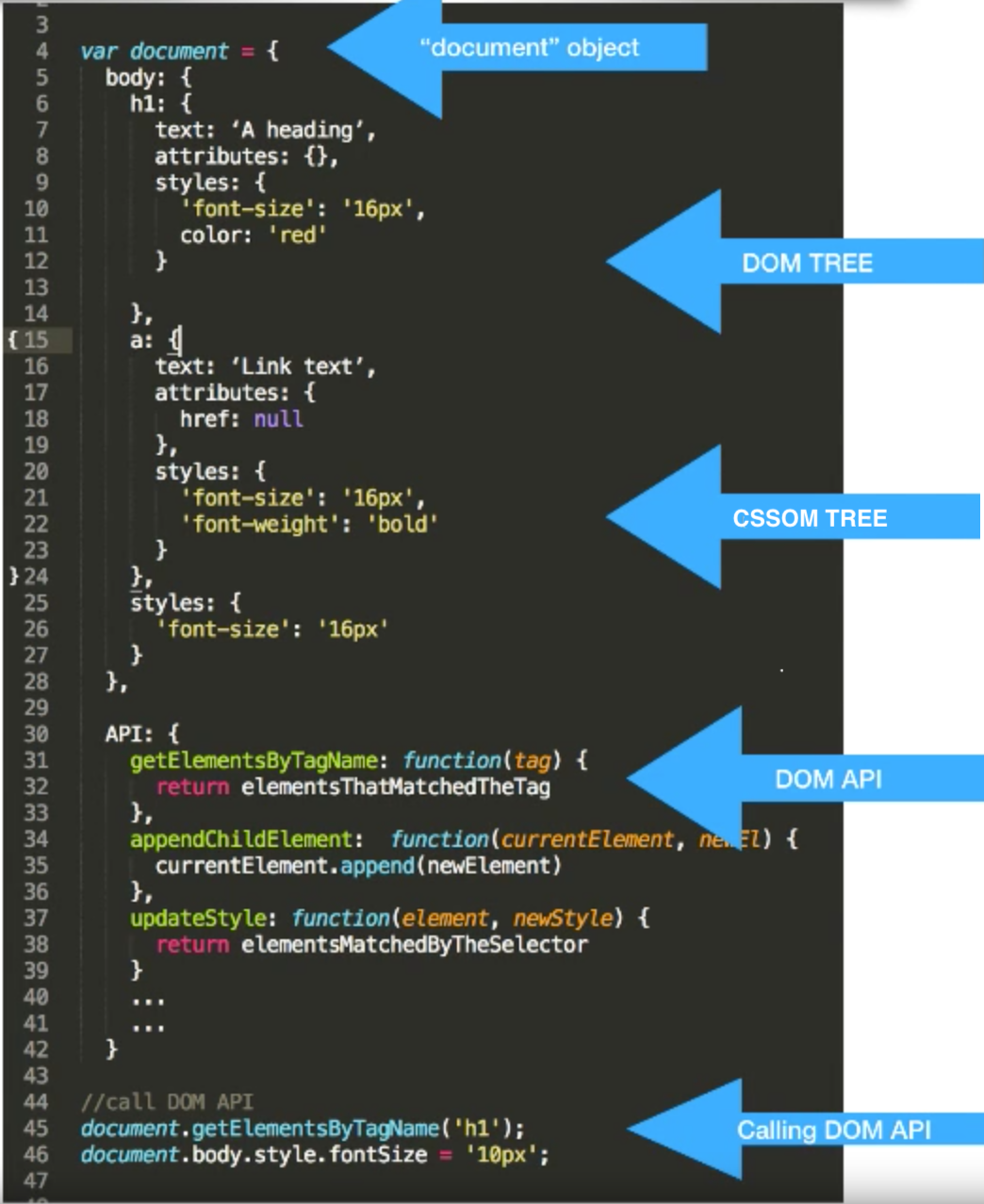
Description of sections of document object:
- DOM TREE: is the tree that contains pure html objects to be drawn
- CSSOM TREE: is the tree that contains CSS objects that are read either from CSS file or in-code CSS tags
- DOM API: is the javaScript functions provided by default, using which we can access DOM-Tree objects. If we add more custom javaScript codes, you can imagine them ending up in this section
Event Manager
Another important concept to know in browser is the Event Manager. Event Manager is responsible to interactive part of the browser, where browser interacts with Operating System by getting ingested various events. Operating System events can be:
- Time change event
- Browser resive event
- Internet (network incoming) event
- Keyboard and mouse event
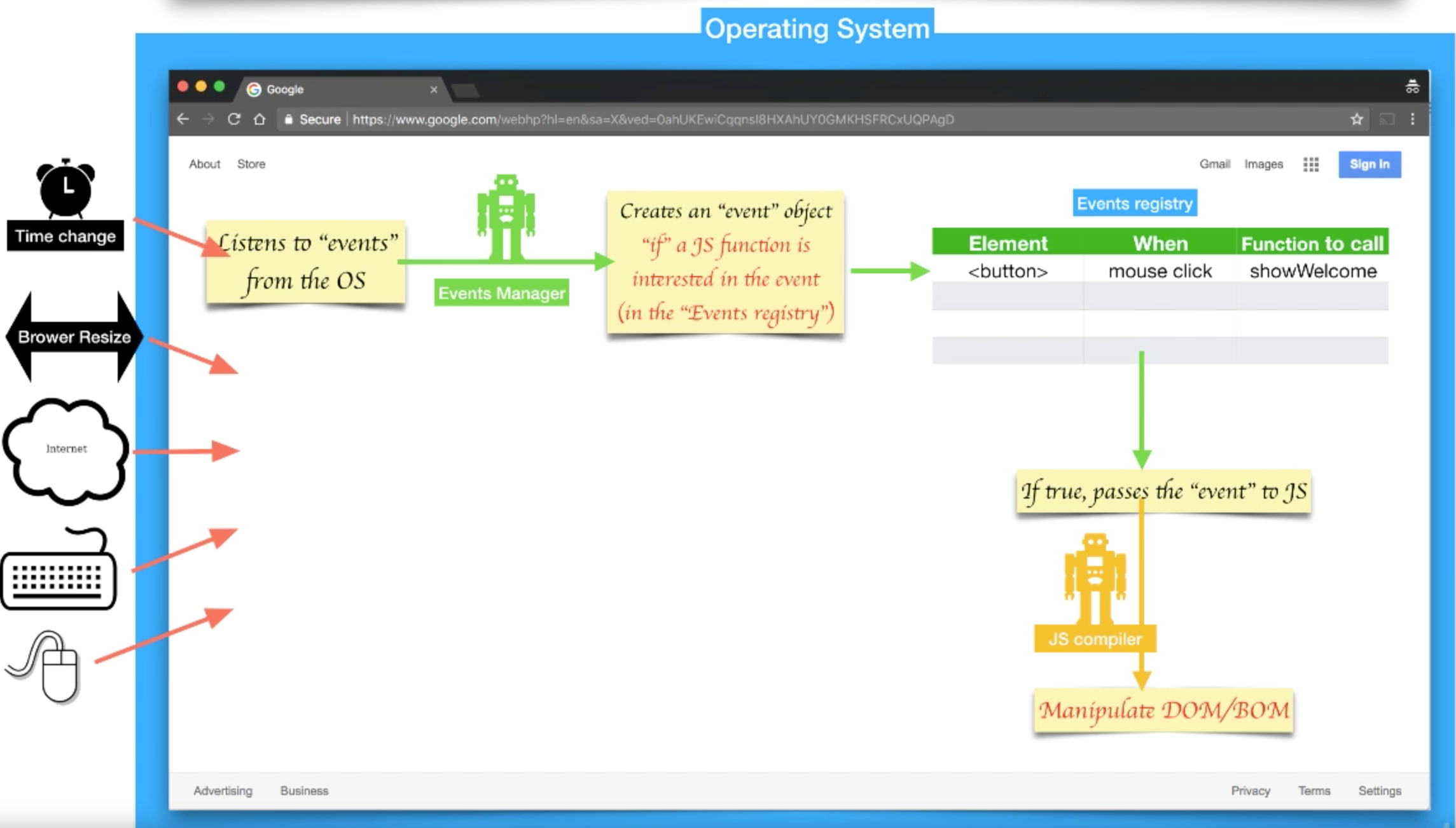
Event-Manager listens for events from OS, when it receives new event it checks Event-Registry table and creates EventObjects only if JS interested in that event. Event-Registry table is filled out when the page is processed first time, if the Document tree object contains some callback event used, then it is registered in Event-Registry table. That way javaScript compiler can perform manipulative actions on DOM/BOM objects whenever external events come in.
Not so clear? lets go step by step explanation of the full cycle of registering and calling events.
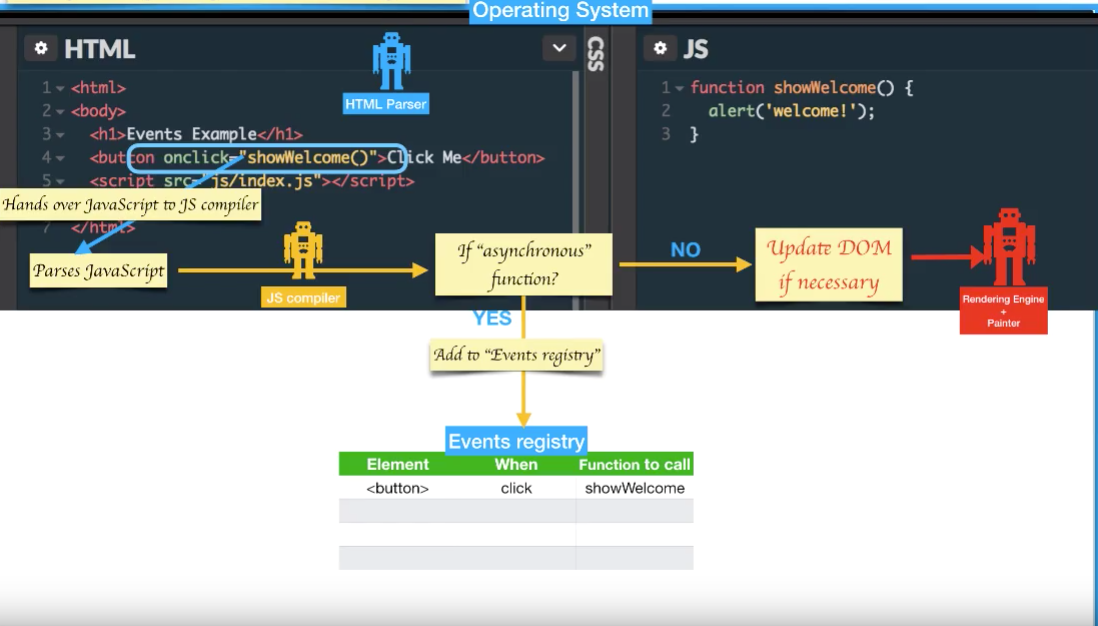
Figure above explains, when compiler sees onclick action assigns showWelcome() function it registers it to Events-Registry table asynchronously.
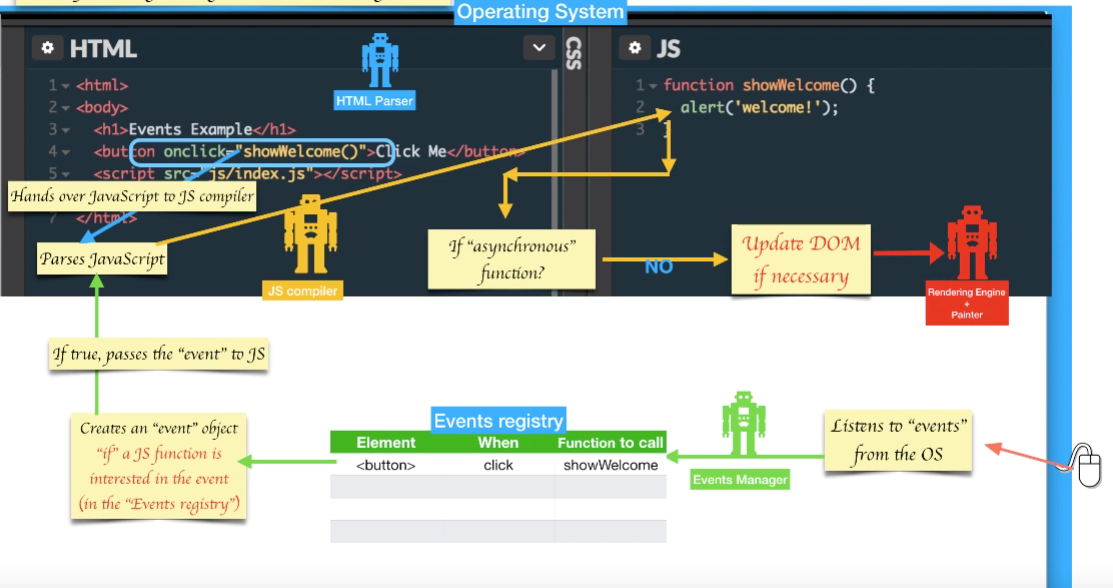
Later when mouse-click action happens it checks the Events-Registry table and sees there is a function to call for mouse click action and goes for triggering showWelcome() function.
There are many kind of JS event objects can be registered in the Event-Registry table, some of them are: MouseEvent, KeyboardEvent, XMLHttpRequestEvent(Ajax) etc.